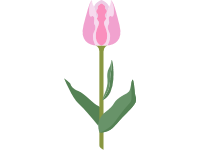
Tulips (Tulipa) form a genus of spring-blooming perennial herbaceous bulbiferous geophytes (having bulbs as storage organs). The flowers are usually large, showy and brightly colored, generally red, pink, yellow, or white (usually in warm colors). They often have a different colored blotch at the base of the tepals (petals and sepals, collectively), internally. Because of a degree of variability within the populations, and a long history of cultivation, classification has been complex and controversial. Tulipa (tulips) is a genus of spring-blooming perennial herbaceous bulbiferous geophytes, dying back after flowering to an underground storage bulb. Depending on the species, tulip plants can be between 10 and 70 cm (4 and 28 inches) high.The tulip's flowers are usually large and are actinomorphic (radially symmetric) and hermaphrodite (contain both male (androecium) and female (gynoecium) characteristics), generally erect, or more rarely pendulous, and are arranged more usually as a single terminal flower, or when pluriflor as two to three (e.g. Tulipa turkestanica), but up to four, flowers on the end of a floriferous stem (scape), which is single arising from amongst the basal leaf rosette. In structure, the flower is generally cup or star shaped. As with other members of Liliaceae the perianth is undifferentiated (perigonium) and biseriate (two whorled), formed from six free (i.e. apotepalous) caducous tepals arranged into two separate whorls of three parts (trimerous) each. The two whorls represent three petals and three sepals, but are termed tepals because they are nearly identical. The tepals are usually petaloid (petal like), being brightly coloured, but each whorl may be different, or have different coloured blotches at their bases, forming darker colouration on the interior surface. The inner petals have a small, delicate cleft at the top, while the sturdier outer ones form uninterrupted ovals.Tulip flowers come in a wide variety of colours, except pure blue (several tulips with 'blue' in the name have a faint violet hue), and have absent nectaries.Tulip flowers are generally bereft of scent and are the coolest of floral characters. The Dutch regarded this lack of scent as a virtue, as it demonstrates the flower's chasteness.