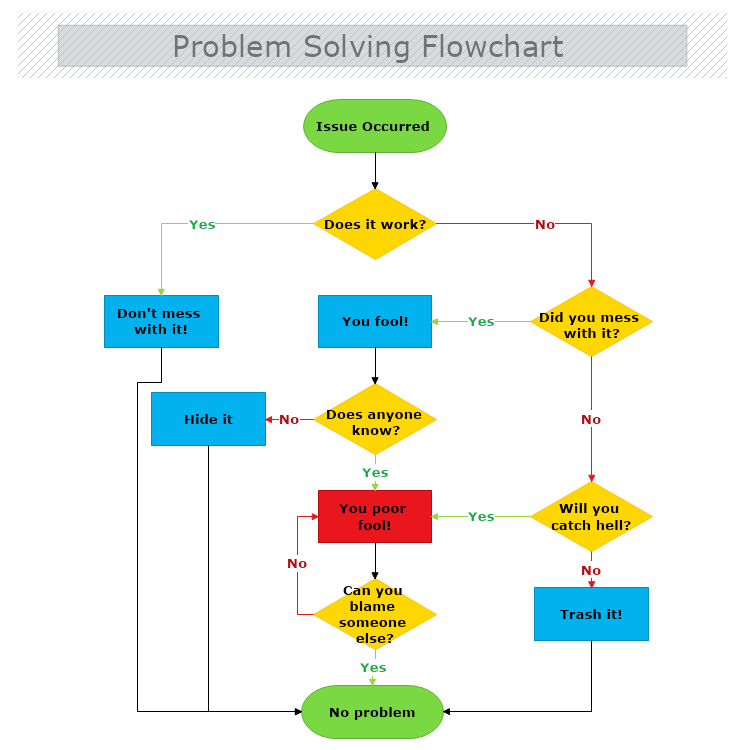
Flowchart diagrams visually illustrate entire processes with all possible outcomes. Flowchart diagrams are used on many occasions for easily describing each stage of a process while taking into account the possible milestones during the process steps. Flowcharts help the development and standardization of the ways a process is performed and eliminate any possible mistakes.
What do you need to create a flowchart diagram?
- Knowledge of the process you will be describing;
- Knowledge of the factors influencing the process;
-
MyDraw for Windows or Mac.
Create a Flowchart diagram step by step
Step 1: Identify the first step from the process
The beginning of the flowchart could be either the first step of the process or the event/need triggering it. For example, the first step of a flowchart describing the process of installing computer software might be to
Download the software or
Insert the software's CD. If a flowchart event starts the flowchart, the first step could be the event itself – e.g. when a problem has arisen and we need to create a flowchart, the steps of which will solve it. In this case, we can simply place
Issue Occurred as the first stage of our flowchart diagram.

Step 2: Continue by noting the immediate actions to follow in the flowchart
Once we have the beginning of the flowchart, the next step is to specify the process being described in the flowchart in detail. This is done via a decision flow that splits the flowchart into smaller and more manageable sub-processes. In our example, the second step of the flowchart is to verify the stage of the problem by answering the question
“Does it work?” (assuming for our flowchart that the problem may be a computer which stopped working).
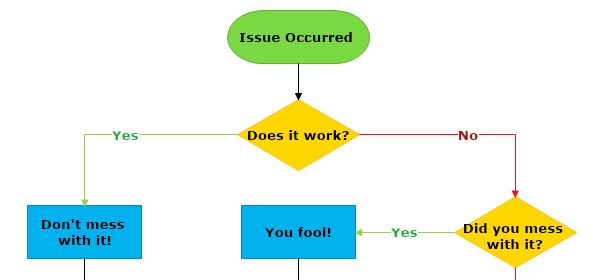
Step 3: Follow through the process and finish the flowchart diagram
From this stage on, the flowchart should dive in detail and describe each following step with all possible outcomes. Flowchart diagrams don’t limit you to only one possible outcome – there can be as many outcomes, as the process requires. In our example, there are two possible outcomes: "You poor fool" and "No problem".