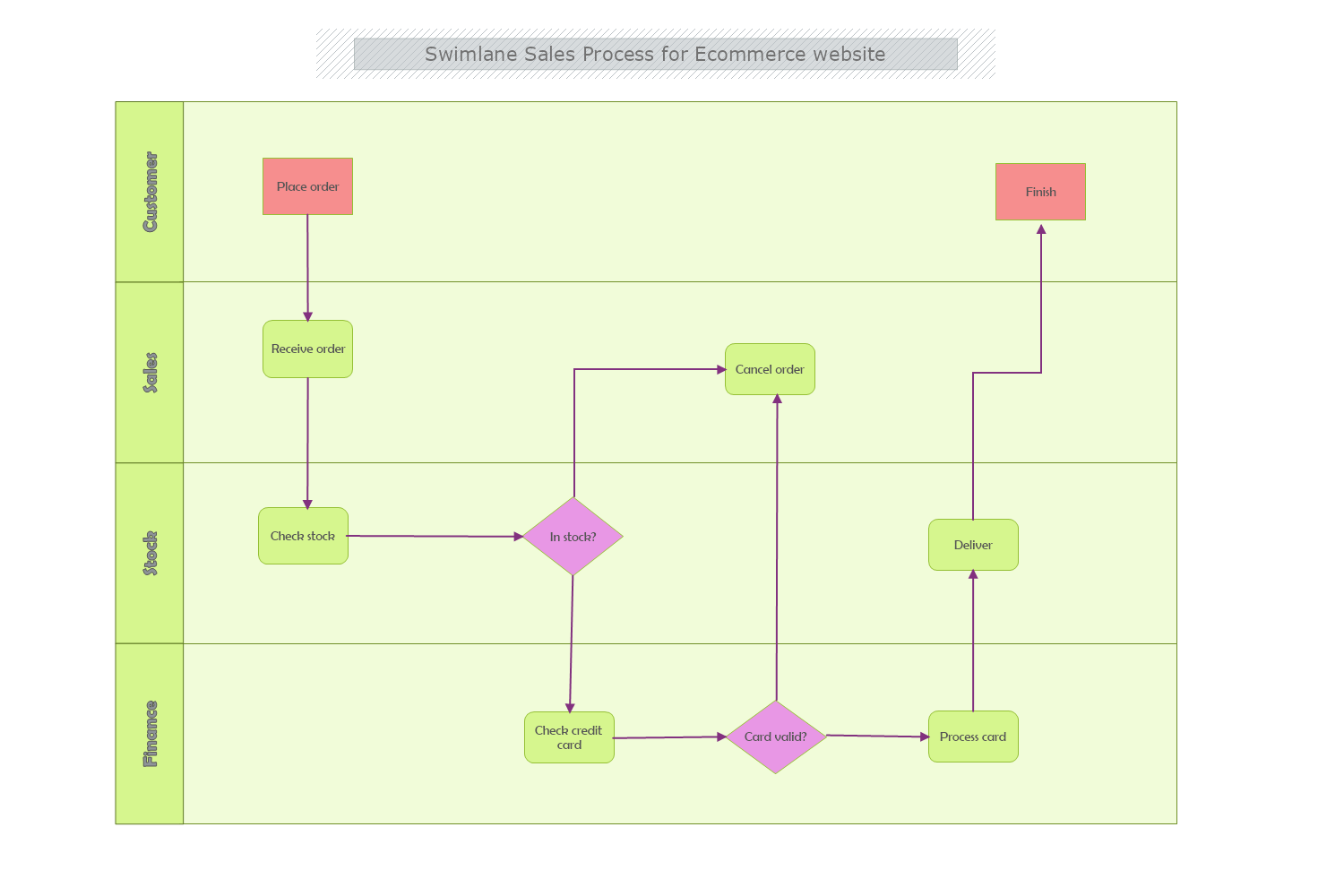
An e-commerce shop functions with the same purpose as a physical store- to sell goods or services to a client. The difference is in the management, distribution, and checks, as it is done in the virtual space but the procedures are more or less the same.
A potential customer visits the online marketplace and browses through a set of items organized in different categories. If you have set for the store to have a profile he/she can put the desired products in a list or basket. At the point of the purchase, he sends a request to the store and chooses a payment method, delivery, picks up from a physical shop, etc. On the other hand, the merchant has to check if item/s are in stock and confirm the order via email or phone call.
Summing up the process: Accept the order> Process the order> Ship/ Send the order.
Before the items are sent the buyer can cancel the order through the online store. Also, most e-commerce shops have a 14-day or longer, depending on the goods/services return policy. In some cases, the taxes are covered by the merchant, but it depends on the occasion and agreed with terms in the policy.
Overall an e-commerce business can save you time and money, expand your customer base and track sales easily. However, it is an investment and has risks. Some challenges can include payment and data fraud, fierce competition, and discount-seeking consumers.